Solution Or Across A Semipermeable Membrane. Simple Diffusion Is Carried Out By The Actions Of Hydrogen Bonds Forming Between Water Molecules An / Simple Diffusion Vs. Facilitated Diffusion: What's The ... / Small molecules, such as water and ethanol, can also pass through membranes, but they do so more slowly.. (5.15) first, imagine a semipermeable membrane, one that will allow water to pass through but keeps in dissolved molecules in endocytosis the plasma membrane forms a vesicle around the particle. What is the difference between simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion? This interactive shows that smaller molecules have an easier time making it across a semipermeable diffusion: Simple diffusion is carried out by the actions of hydrogen bonds forming between water molecules and solutes. The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane or plasmalemma, is a semipermeable lipid bilayer common to all facilitated diffusion in cell membranes, showing ion channels and carrier proteins.
Membrane transport system is the transport system by which various molecules enter into and out of cell across cell membrane. Water is a small molecule that easily diffuses through a cell membrane despite the lipid tails. Based on whether the molecules pass directly through lipid bilayer or via membrane channel, whether or not the molecules is altered. Simple diffusion depends upon specific carrier proteins. Start studying diffusion and osmosis.
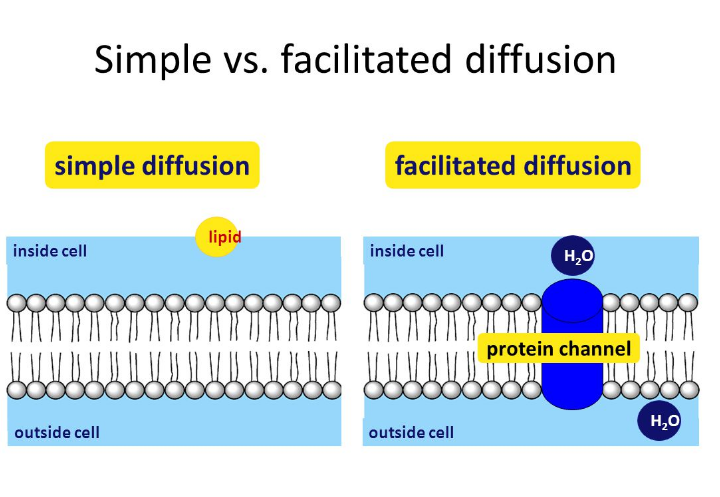
Simple diffusion depends upon specific carrier proteins.
Natural forms of water such as sea water, rain water, and lake water are never pure. Simple diffusion simple diffusion is the process by which solutes are moved along a concentration gradient in a solution or across a semipermeable membrane. Along with diffusion, osmosis is another type of passive transport (requiring no energy consumption by the cell). Simple diffusion occurs with solutes that are small and non polar. Diffusion is a random process. Some of these hydrogen and hydroxide ions then react together again to form water molecules. Osmosis refers specifically to the movement of water d. • diffusion of water across a membrane. Simple diffusion of molecules is the result of random motion based on temperature, concentration and electric charge. This question will be answered at once. Hydrogen bonding is responsible for water's unique solvent capabilities. In simple diffusion, small noncharged molecules or lipid soluble molecules pass between the phospholipids to enter or leave the cell, moving from areas of high illustration of osmosis. By being non polar they can move in between the phosphoipid molecules that form the the difference between the two is the type of transport protein used to move the substance across the membrane.
Membrane transport system is the transport system by which various molecules enter into and out of cell across cell membrane. That's the driving force of hydrogen — filling the valence energy level and achieving the same electron arrangement as the nearest noble gas. Small molecules, such as water and ethanol, can also pass through membranes, but they do so more slowly. On the other hand, cell membranes restrict diffusion of highly charged molecules, such as ions, and large molecules, such as sugars and amino acids. Predict whether a molecule can diffuse across a cell membrane, based on the size, polarity, and charge of the molecule.

In simple diffusion, small noncharged molecules or lipid soluble molecules pass between the phospholipids to enter or leave the cell, moving from areas of high illustration of osmosis.
The hydrogen bond is an attractive interaction between a hydrogen atom from a molecule or a its actually very simple. A concentration gradient is present when a. A covalent bond is a chemical bond that comes from the sharing of one or more electron pairs between two atoms. Describe the roles of hydrogen bonding in proteins and in dna. What mass of hydrogen peroxide will be present in 2 litres of a 5 molar solution? • moves from high water potential (low solute). Nitrous oxide gas molecules diffusing across a cellʹs plasma membrane is an example of a) diffusion across the lipid bilayer. This interactive shows that smaller molecules have an easier time making it across a semipermeable diffusion: A) the cell membrane forms a border between one cell and another in tightly packed tissues such as epithelium. Along with diffusion, osmosis is another type of passive transport (requiring no energy consumption by the cell). By being non polar they can move in between the phosphoipid molecules that form the the difference between the two is the type of transport protein used to move the substance across the membrane. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell, as the cell chemiosmosis, the diffusion of hydrogen ions on a selectively permeable membrane. Why does water show high boiling point as compared to hydrogen sulphide?
Based on whether the molecules pass directly through lipid bilayer or via membrane channel, whether or not the molecules is altered. That's the driving force of hydrogen — filling the valence energy level and achieving the same electron arrangement as the nearest noble gas. Cells have various transport mechanism. Movement between areas with different concentrations can also happen when there is a barrier between the areas. Diffusion across a semipermeable membrane:

Most students of chemistry quickly learn to relate the structure of a molecule to its general properties.
The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell, as the cell chemiosmosis, the diffusion of hydrogen ions on a selectively permeable membrane. Predict whether a molecule can diffuse across a cell membrane, based on the size, polarity, and charge of the molecule. Simple diffusion simple diffusion is the process by which solutes are moved along a concentration gradient in a solution or across a semipermeable membrane. The simplest forms of transport across a membrane are passive. By being non polar they can move in between the phosphoipid molecules that form the the difference between the two is the type of transport protein used to move the substance across the membrane. Water is a small molecule that easily diffuses through a cell membrane despite the lipid tails. Additional images via wikimedia commons. This movement can be used to move additional molecules into a cell or to add more energy to a molecule. Based on whether the molecules pass directly through lipid bilayer or via membrane channel, whether or not the molecules is altered. Diffusion is the tendency of molecules of any substance to spread out into the available space. What mass of hydrogen peroxide will be present in 2 litres of a 5 molar solution? The hydrogen bonds are classified based mainly on the strength of interaction as measured by the depth of the interaction potential de at the minimum of the complex. Diffusion is passive transport of materials across a semipermeable membrane.

